Are you looking for a flexible, scalable and affordable solution for getting token prices
on chain? In this article we will show you how to can make your own dedicated price feed
oracle using the Kenshi Oracle Network.

How to deliver price data to your smart contract?
To create your custom oracle with the Oracle Network, you can use your preferred programming language.
In this tutorial we will use JavaScript. We will also write a sample smart contract in Solidity
that will interact with your new oracle. I will show you how to code, create and deploy your price
feed oracle and guide you through the best security practices.
This tutorial uses the CoinGecko APIs for getting the token prices, but you can use any
other API as you see fit. I will also use Vercel to deploy the oracle, but you can host
it anywhere else. To follow this tutorial, you can create a free Vercel account.
First you will need a smart contract that talks to your oracle and requests price data, so let's make
a simple contract that does just that. Let's create a barebone contract first:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.17;
contract Price {
address private _owner;
constructor() {
_owner = msg.sender;
}
}Now you need a function that emits an event requesting the price data. Let's add this function
and the corresponding event:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.17;
contract Price {
address private _owner;
constructor() {
_owner = msg.sender;
}
// A simple event to make price data requests
event PriceRequest();
/**
* Emit an event that will be picked up by the Kenshi
* Oracle Network and sent to your oracle for processing
*/
function requestPrice() external {
emit PriceRequest();
}
}Next you will need a callback function that your oracle will call to deliver the requested price data,
and another function to show the price once it is delivered:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.17;
contract Price {
uint256 private _price;
address private _owner;
constructor() {
_owner = msg.sender;
}
// A simple event to make price data requests
event PriceRequest();
/**
* Emit an event that will be picked up by the Kenshi
* Oracle Network and sent to your oracle for processing
*/
function requestPrice() external {
emit PriceRequest();
}
/**
* This method will be called by the Kenshi Oracle Network
* with the result returned from your oracle
*/
function setPrice(uint256 price) external {
_price = price;
}
/**
* This function simply returns the price set by the oracle
*/
function getPrice() external view returns (uint256) {
return _price;
}
}Let's add some security to the contract and verify that your oracle, not an attacker, is
calling your callback:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.17;
contract Price {
uint256 private _price;
address private _owner;
address private _oracle;
constructor() {
_owner = msg.sender;
}
/**
* Sets the oracle address to prevent anyone else from
* calling the "setPrice" method
*/
function setOracle(address oracle) external {
require(msg.sender == _owner, "Only owner can call this");
_oracle = oracle;
}
// A simple event to make price data requests
event PriceRequest();
/**
* Emit an event that will be picked up by the Kenshi
* Oracle Network and sent to your oracle for processing
*/
function requestPrice() external {
emit PriceRequest();
}
/**
* This method will be called by the Kenshi Oracle Network
* with the result returned from your oracle
*/
function setPrice(uint256 price) external {
require(msg.sender == _oracle, "Only oracle can call this");
_price = price;
}
/**
* This function simply returns the price set by the oracle
*/
function getPrice() external view returns (uint256) {
return _price;
}
}You can now head over to Remix IDE and deploy the above smart contract:
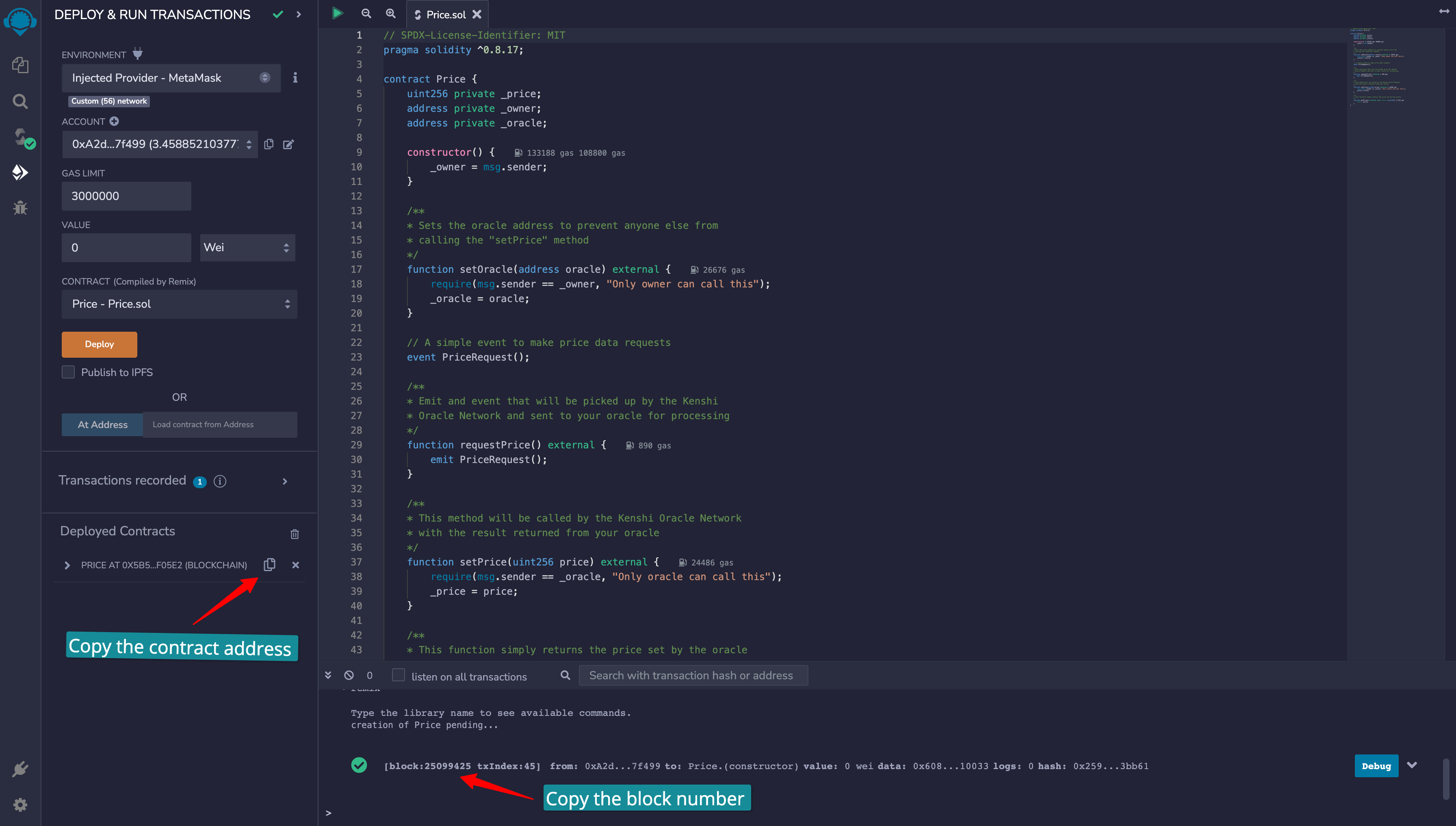
Deploy with Remix and copy the deployment details
Copy the deployed contract address and the block number where we deployed the contract
somewhere safe, as you will need them later.
The first thing you need is to set up your project tree. Run the following commands to
create a npm project and install the required dependencies:
mkdir coingecko-oracle
cd coingecko-oracle
npm init -y
npm i -S ethers node-fetch
mkdir api
touch api/oracle.jsYour oracle logic should go to the "api/oracle.js" file. Now you need a function that
fetches the token price you are interested in from CoinGecko API endpoints. In this
function, you want to get an average price of your token.
You could also use the spot price of the token, but that would make your oracle vulnerable
to price manipulation attacks. For example, an attacker could create a transaction to change
the token price in their favor, interact with your oracle, benefit, and finally make another
transaction to revert the token price to its original value.
Here's a sample function that fetches price data for the Kenshi token and calculates its
30-minute average:
import fetch from "node-fetch";
const url =
"https://api.coingecko.com/api/v3/coins/kenshi/market_chart?vs_currency=usd&days=1";
const fetchPrice = async () => {
const resp = await fetch(url);
const { prices } = await resp.json();
const slice = prices.slice(-6); // last 30 minutes
const average = slice.map(([_, price]) => price).reduce((a, b) => a + b) / 6;
return average;
};You also need to implement the Kenshi Oracle Network protocol. You only need a simple HTTP
server that tells the Oracle Network what to do with the incoming request. You need to tell
the Oracle network which function on your smart contract it should call, what arguments it
should pass to the function, and how much gas it is allowed to spend.
Using Vercel, you can do the following to achieve this:
import fetch from "node-fetch";
import { ethers } from "ethers";
const url =
"https://api.coingecko.com/api/v3/coins/kenshi/market_chart?vs_currency=usd&days=1";
const fetchPrice = async () => {
const resp = await fetch(url);
const { prices } = await resp.json();
const slice = prices.slice(-6); // last 30 minutes
const average = slice.map(([_, price]) => price).reduce((a, b) => a + b) / 6;
return average;
};
export default async function handler(request, response) {
const price = await fetchPrice();
response.status(200).json({
method: "setPrice",
args: [ethers.utils.parseUnits(price.toFixed(18)).toString()],
maxGas: "10000000000000000", // 0.01 ETH
abort: false,
});
}To deploy the oracle, you can run this command at the root of the project and follow
the instructions:
vercel .You should see an output like this:
➜ vercel .
Vercel CLI 23.1.2
? Set up and deploy “~/Projects/kenshi/coingecko-oracle”? [Y/n] y
? Which scope do you want to deploy to? *****
? Link to existing project? [y/N] n
? What’s your project’s name? coingecko-oracle
? In which directory is your code located? ./
No framework detected. Default Project Settings:
- Build Command: `npm run vercel-build` or `npm run build`
- Output Directory: `public` if it exists, or `.`
- Development Command: None
? Want to override the settings? [y/N] n
🔗 Linked to *****/coingecko-oracle (created .vercel and added it to .gitignore)
🔍 Inspect: https://vercel.com/*****/coingecko-oracle/******** [1s]
✅ Production: https://coingecko-oracle.vercel.app [copied to clipboard] [13s]
📝 Deployed to production. Run `vercel --prod` to overwrite later (https://vercel.link/2F).Copy and keep the deployment URL safe, as you will need it later.
You're now ready to create your oracle on the Kenshi Oracle Network. Head to the Kenshi Oracle Network
dashboard and click the "Create Oracle" button. Fill out the form as follows:
- Select your smart contract chain (BNB Smart Chain for this example) from the "Blockchain" dropdown and input your deployed contract address in the "Contract address" field.
- Enter the block number of your smart contract into the "Block" field under the "Starting point" section. This field tells the Oracle Network to look for price data requests starting from that block.
- In the "Endpoint" field under the "Oracle logic" section, enter the deployment address you got from Vercel.
- Input the human-readable ABI of your contract into the form's "ABI" field.
- Enter the event signature defined in your smart contract into the "Signature" field.
- Finally, you can decide on how many months and for how many requests the Oracle Network should keep your oracle alive.
The filled form should look similar to this, except for the contract address and the oracle
logic endpoint:
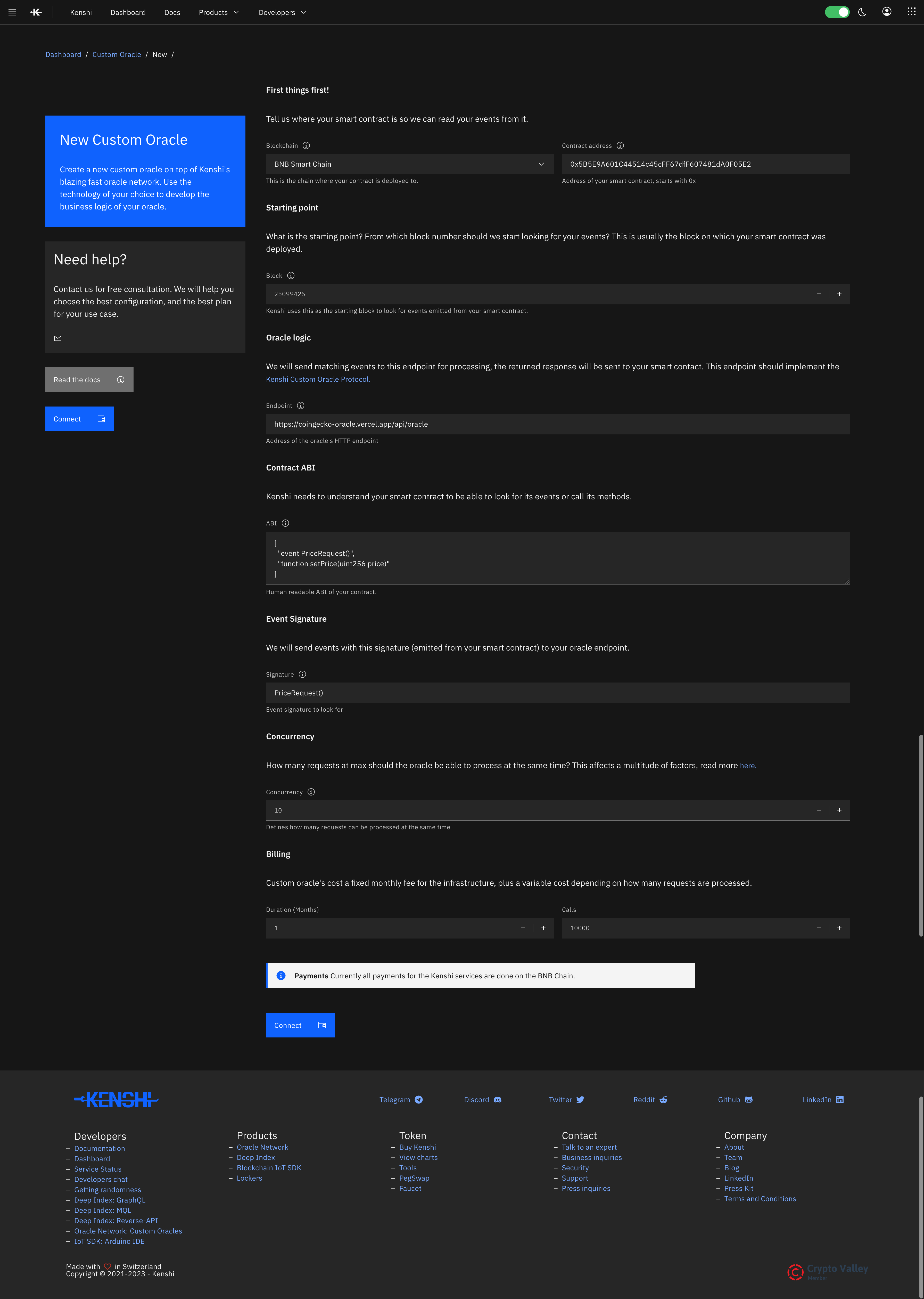
Your custom oracle filled form should look like this
Once deployed, go to the oracle admin page on the Kenshi Oracle Network dashboard and copy
the gas (sender) address of your oracle from the "Add Credit" tab:
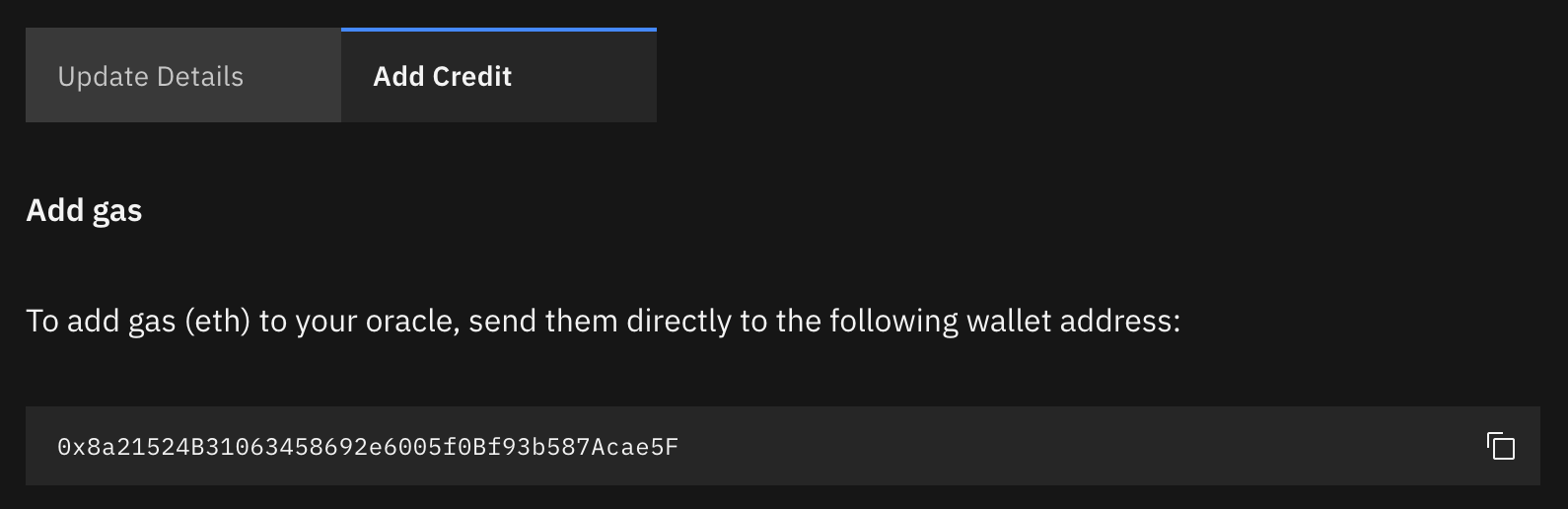
Get the oracle's gas (sender) address here
You need to transfer a little bit of gas to your oracle so it can fulfill price data requests:
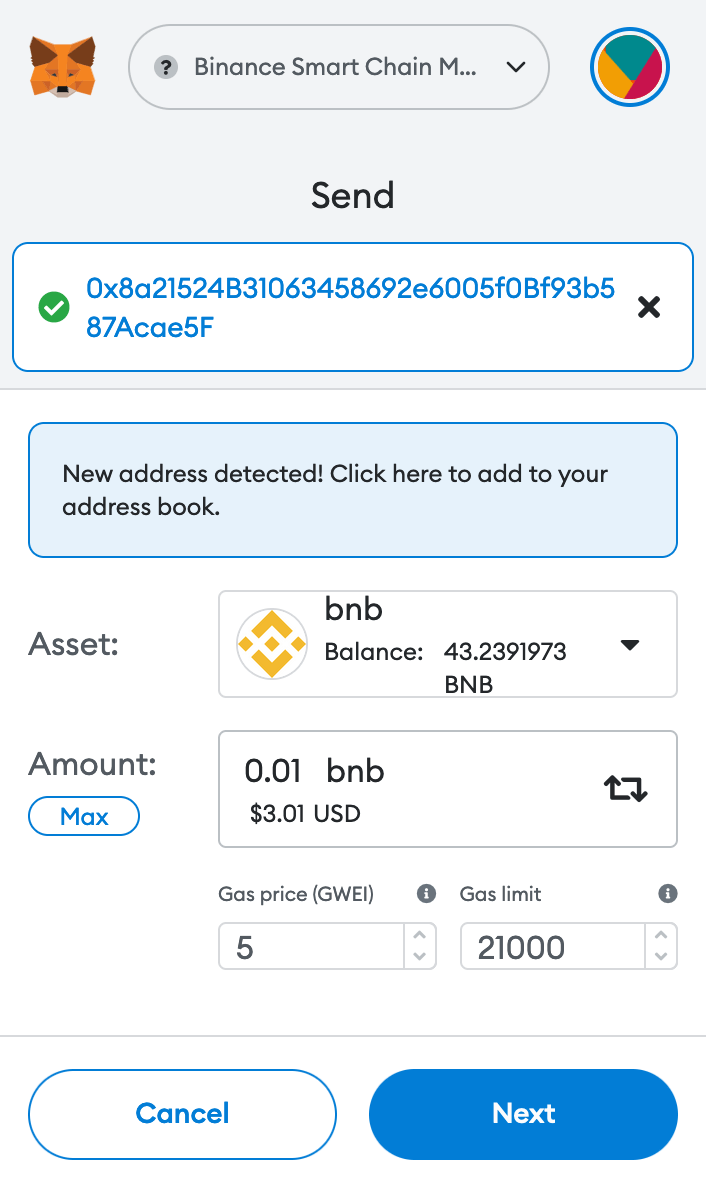
And finally, you will need to authorize the oracle address in your smart contract:
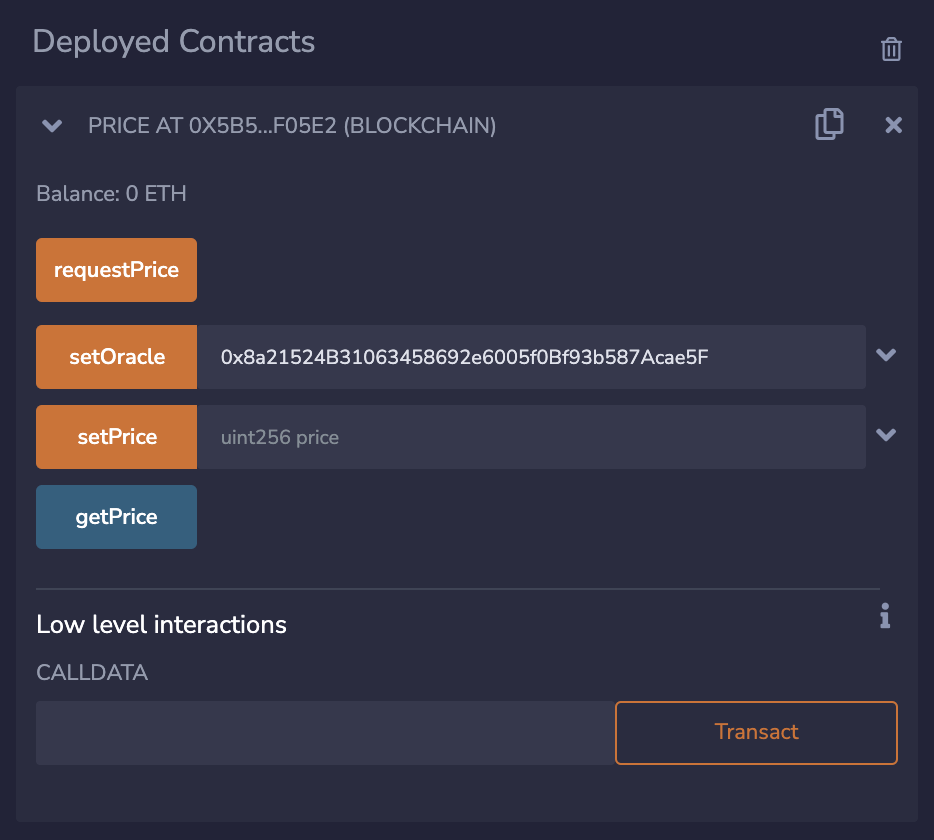
Now you can call the "requestPrice" function of the contract, and assuming you followed all the previous steps,
the oracle should send you a response:
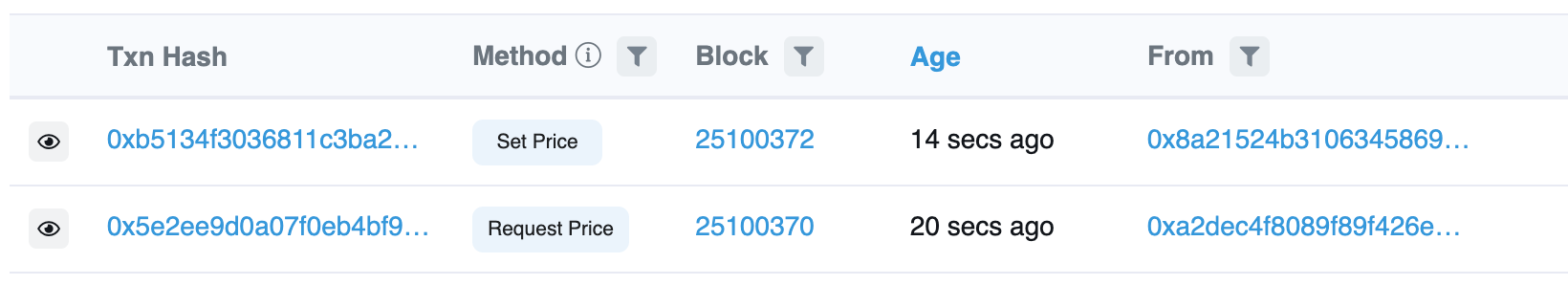
Kenshi Oracle Network has hyper-fast response times
You should be able to see the retrieved token price now:
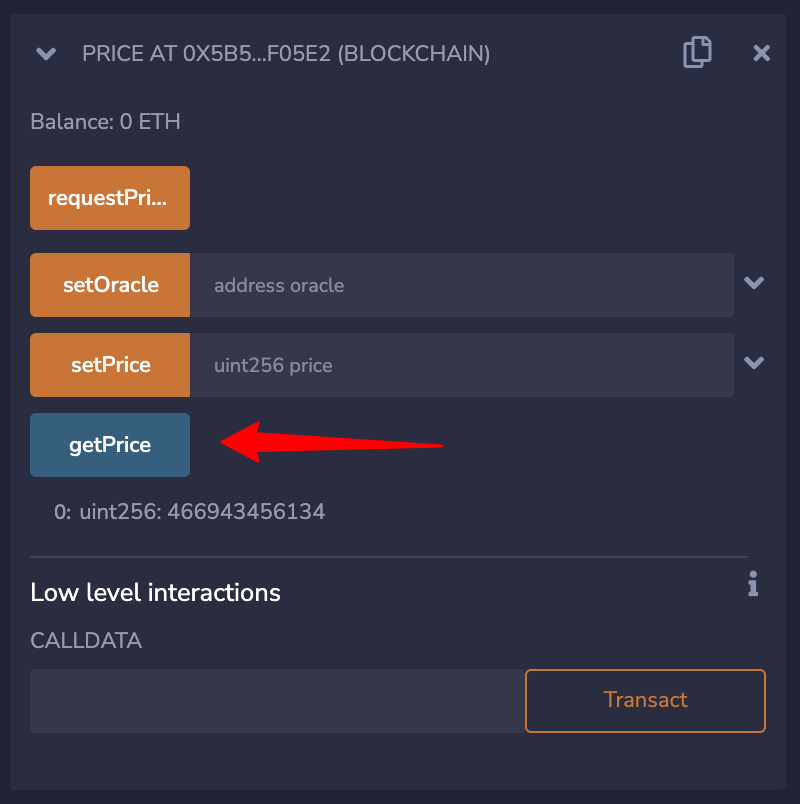
In this article we demonstrated a simple price feed oracle, however the possibilities of the Kenshi Oracle Network
are limitless! Be sure to follow us on Twitter if you want more news about Kenshi or more awesome articles about
the Kenshi Oracle Network.
You can view the source code of this sample oracle
here on GitHub .
